
PRODUCTS
Soy lecithin liquid is a natural lecithin mixture e……

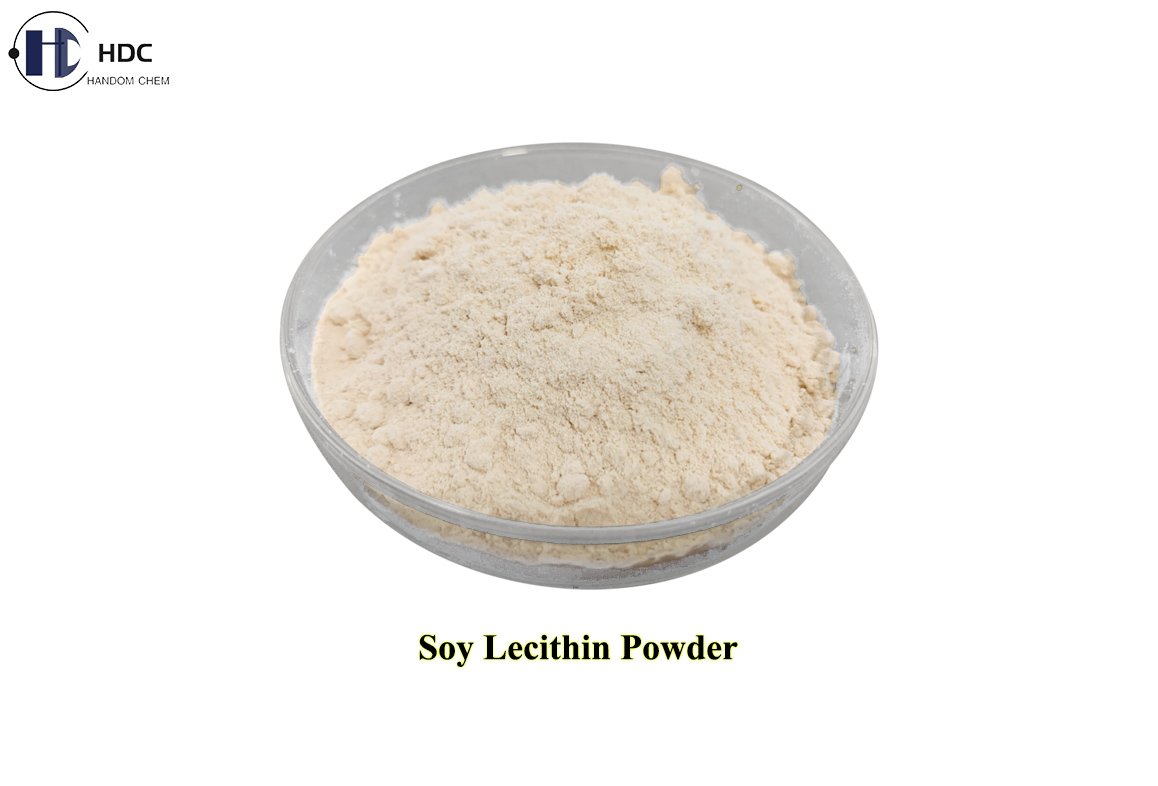
Soybean lecithin powder, also called soya lecithin ……

Product Name: Chitosan AzelateGrade: Cosmetic Grade……

Commodity Name: IscotrizinolChemical Name: Diethylh……

Brief Introduction:
Plant cholesterol is a substance similar to cholesterol that exists in plants, the scientific name is Phytosterol. Phytosterol is an active ingredient in plants and is very beneficial to human health.
Studies have found that phytosterols have the effects of lowering blood cholesterol, inhibiting breast hyperplasia and regulating immunity. Among them, lowering cholesterol is the most certain conclusion. Domestic and foreign studies have shown that phytosterols can compete with cholesterol in the intestines, reduce cholesterol absorption, and effectively reduce the content of "bad" cholesterol (total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol) in the blood of patients with hyperlipidemia without affecting the content of "good" cholesterol (high density lipoprotein cholesterol) in the blood. Therefore, it has a good lipid-lowering effect on patients with hyperlipidemia.
According to statistics, the more phytosterols are consumed in the diet, the less risk of heart disease and other chronic diseases.
At present, many international organizations and scholars recommend the intake of foods high in phytosterols to reduce the occurrence of chronic diseases such as coronary heart disease.
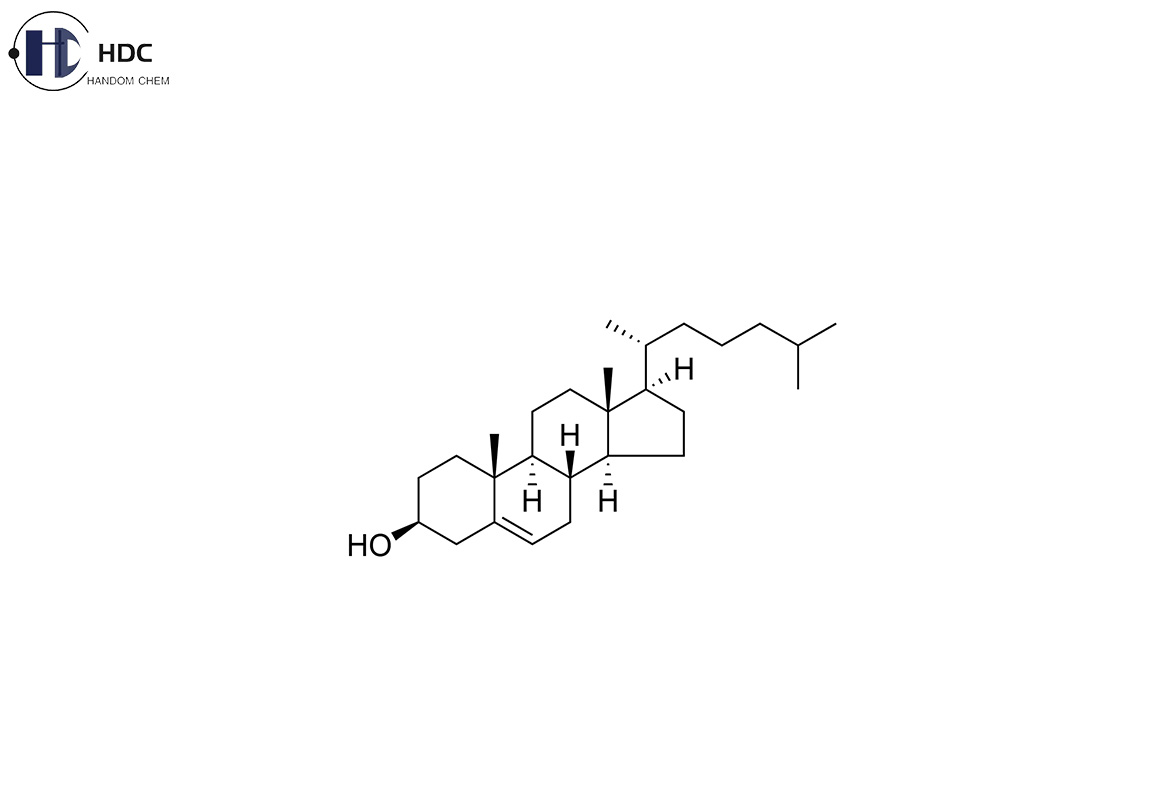
Health-Promoting Properties of Plant-Source Cholesterol:
1. Cardiovascular Health:
The effects of plant-based cholesterol on cardiovascular health are profound. Many studies have demonstrated their ability to lower Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol(LDL-C), thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Plant-based cholesterol helps maintain a healthy lipid profile, which is a key factor in preventing heart-related complications.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects:
In addition to its cholesterol-lowering properties, plant origin cholesterol also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is associated with a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and certain cancers. The ability of plant-derived cholesterol to modulate inflammatory responses demonstrates its potential in the prevention and management of inflammatory diseases.
3. Antioxidant Activity:
Plant-derived cholesterol also has antioxidant properties, which helps to scavenge free radicals from the body. This antioxidant activity helps protect cells, slows down the onset of oxidative stress, and may play a role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases associated with oxidative damage.
Specifications of our Plant-derived Cholesterol:
Test Items
Specifications
Test Methods
Appearance
White powder or flake crystal
Visual
Identification
Complies with the reference substance structure
IR
Complies with the reference substance structure
TLC
Passes the test
Colour Reaction A
Passes the test
Colour Reaction B
Purity
Not less than 98.0%
HPLC
Assay (HPLC)
95.0% ~ 115.0%
HPLC
Assay (GC)
95.0% ~ 102.0%
GC
Related Substances
Cholesterol Impurity-2
Not more than 0.60%
HPLC
Other single impurity
Not more than 0.50%
HPLC
Total impurities
Not more than 2.0%
HPLC
Acidity
Not more than 0.3 mL
Titration Method
Residue on Ignition
Not more than 0.1%
USP<281>/ChP0841
Optical Rotation
-34.0° ~ -38.0°
USP<781>/ChP0621
Loss on Drying
Not more than 0.30%
USP<731>/ChP0831
Melting Point
147℃ ~ 150℃
USP<741>/ChP0612
Peroxide Content
Not more than 6.00%
USP<401>/ChP0713
Residual Solvents
Dichloromethane
Not more than 600 ppm
GC
Methanol
Not more than 3000 ppm
GC
Sum
Not more than 0.5%
GC
Bacterial Endotoxin
Not more than 0.1 EU/mg
USP<85>/ChP1143
Microbial Limits
Total Aerobic Microbial Count
Not more than 100 CFU/g
USP<61>/ChP1105
Total combined Yeasts and Mold Count
Not more than 10 CFU/g
USP<61>/ChP1105
Heavy Metals
Not more than 10 ppm
USP<231>/ChP0821
Arsenic (As)
Not more than 2 ppm
USP<211>/ChP0822
Nickel (Ni)
Not more than 1 ppm
USP<233>/ChP0412
Solubility in ethanol
Must not be sedimented or cloudy
Visual
Moisture
Not more than 1.00%
KF
Application of Plant-Derived Cholesterol:
1. Functional Foods and Fortified Products:
Incorporating plant-derived cholesterol into functional foods and fortified products has become a trend. For example, plant-derived cholesterol is added to products such as margarine, spreads, and plant milks, providing consumers with a convenient way to increase their daily intake. These products are suitable for individuals who want to manage their cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
2. Dietary Supplements:
Dietary supplements are another way to use plant-based cholesterol, they are usually provided in capsule or liquid form. These supplements provide an option for those who want to increase their intake of plant-based cholesterol in a more direct way.
3. Medicine:
Since plant-derived cholesterol does not have the potential risk of carrying animal viruses like animal-derived cholesterol, it can be used as an excipient for high-end preparations: small molecule liposome drugs, nucleic acid drugs, mRNA vaccines, and non-animal-derived cell culture media for protein drugs.
Packaging:
1g/Bottle, 3g/Bottle, 5g/Bottle, 10g/Bottle, 100g/Bag or according to the specific requirements from customers.
Recommended Storage Conditions:
For short-term storage, it is recommended to store at 2℃ ~ 8℃; it is recommended to keep at -25℃ ~ -15℃ under an inert atmosphere for long-term storage.
For reducing the absorption of the moisture, it should be slowly warmed to ambient temperature before opened.
Shelf Life:
24 months if stored under above mentioned conditions.